In an increasingly interconnected world, the importance of safeguarding our digital lives has never been more critical. As we navigate the vast landscape of the internet, our personal and sensitive information often dwells in environments vulnerable to breaches and misuse. Incident Response Blog of technology has brought immense convenience, but it also presents a myriad of challenges in protecting our privacy and ensuring robust cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity and privacy laws have emerged as vital tools for individuals, businesses, and governments striving to create a safer digital ecosystem. These laws aim to establish regulations that protect users from data theft, cyberattacks, and unauthorized surveillance, while also addressing the responsibilities of entities that handle personal information. Understanding the nuances of these laws is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the digital frontier and maintain control over their privacy in the 21st century.
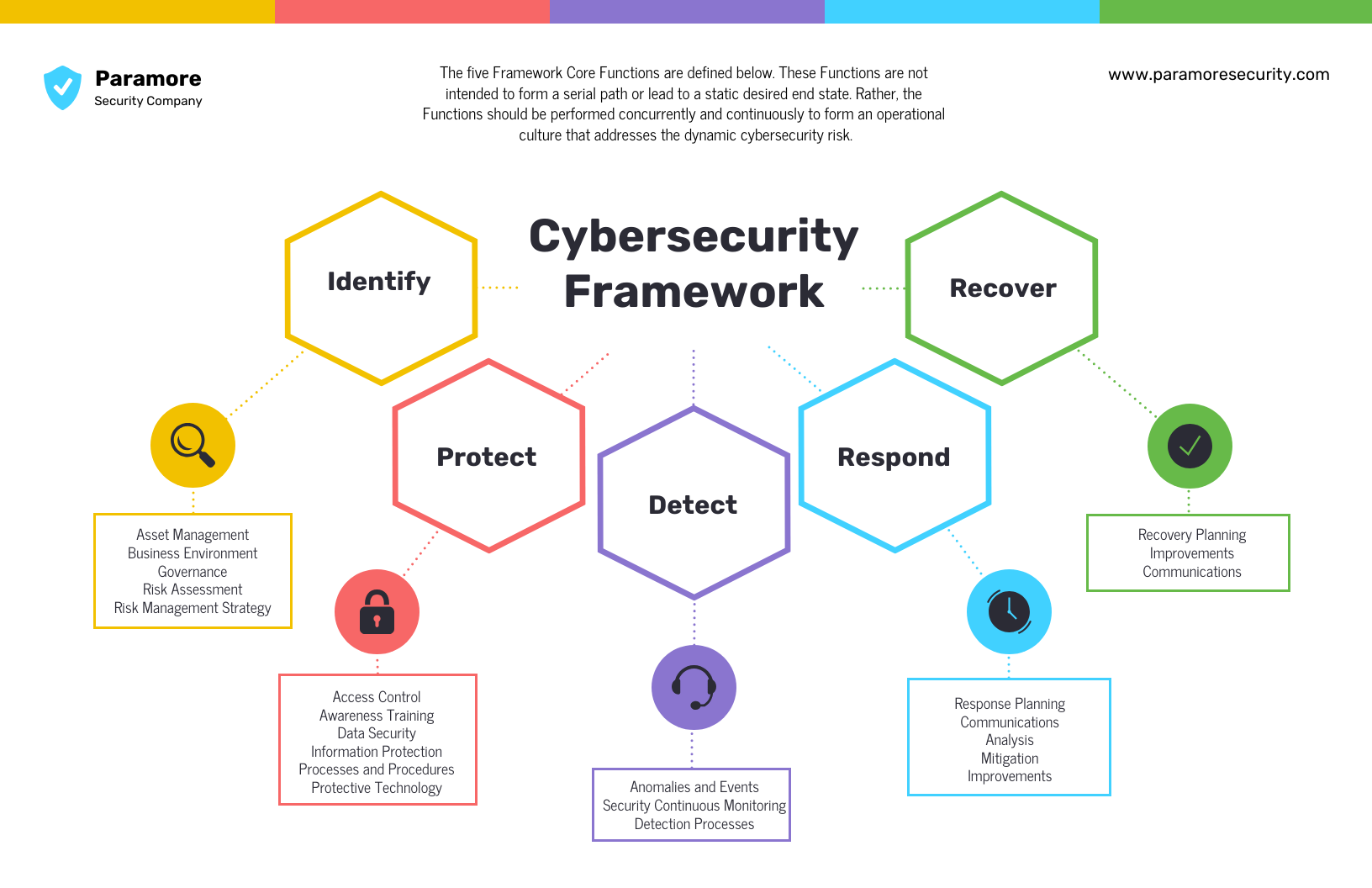
Current Cybersecurity Regulations
In recent years, the increasing frequency and severity of cyber attacks have led governments around the world to implement stricter cybersecurity regulations. One of the prominent frameworks in the United States is the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA), which requires federal agencies to secure their information systems. Additionally, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed guidelines for improving cybersecurity, known as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, which organizations can use to manage and reduce cybersecurity risk effectively.
In Europe, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has transformed the landscape of data privacy and protection. This regulation mandates that organizations handling personal data implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure a high level of security. The GDPR has far-reaching implications for companies operating in or with the European Union, emphasizing the need for robust data protection strategies. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, motivating businesses to prioritize cybersecurity.
Moreover, various sectors have their own specific regulations that dictate cybersecurity requirements. For instance, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) imposes strict data security regulations on healthcare organizations, aiming to protect sensitive patient information. Financial institutions are governed by the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), which requires them to establish safeguards for customer data. These targeted regulations reflect the understanding that different industries face unique risks and require tailored approaches to cybersecurity.
Privacy Laws in the Digital Age
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, privacy laws have become essential in protecting personal information. With the rise of the internet and the increasing dependence on technology, individuals are more vulnerable to data breaches and unauthorized data collection. Laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States set robust standards for the handling of personal data, empowering users to have greater control over their information. These regulations mandate transparency from businesses regarding how they collect, store, and utilize consumer data, fostering a culture of accountability.
Additionally, privacy laws are continually adapting to address emerging technologies and practices. With advancements in artificial intelligence and big data analytics, legislators face the challenge of creating regulations that can keep pace with innovation while still safeguarding individual rights. New frameworks are being considered globally to ensure that as technology evolves, so too does the legal infrastructure designed to protect privacy. This also includes addressing issues related to cross-border data transfers, as companies often operate in multiple jurisdictions.
The enforcement of privacy laws is crucial to their effectiveness. Regulatory bodies play a vital role in ensuring compliance and can impose significant penalties for violations. Friction exists between maintaining user privacy and allowing businesses to leverage data for competitive advantages. Striking the right balance is fundamental to fostering trust between consumers and companies. As society becomes more aware of privacy issues, the demand for robust enforcement mechanisms increases, pushing businesses to prioritize ethical data practices in their operations.
